Engine F1
When you watch Formula 1, it is not only the speed and excitement that impress, but also the technology behind the cars. The engines are the beating heart of F1 cars and provide the enormous power needed to race the cars. In this article, we will explain how the engine of a Formula 1 car works and which components all contribute to the final performance.
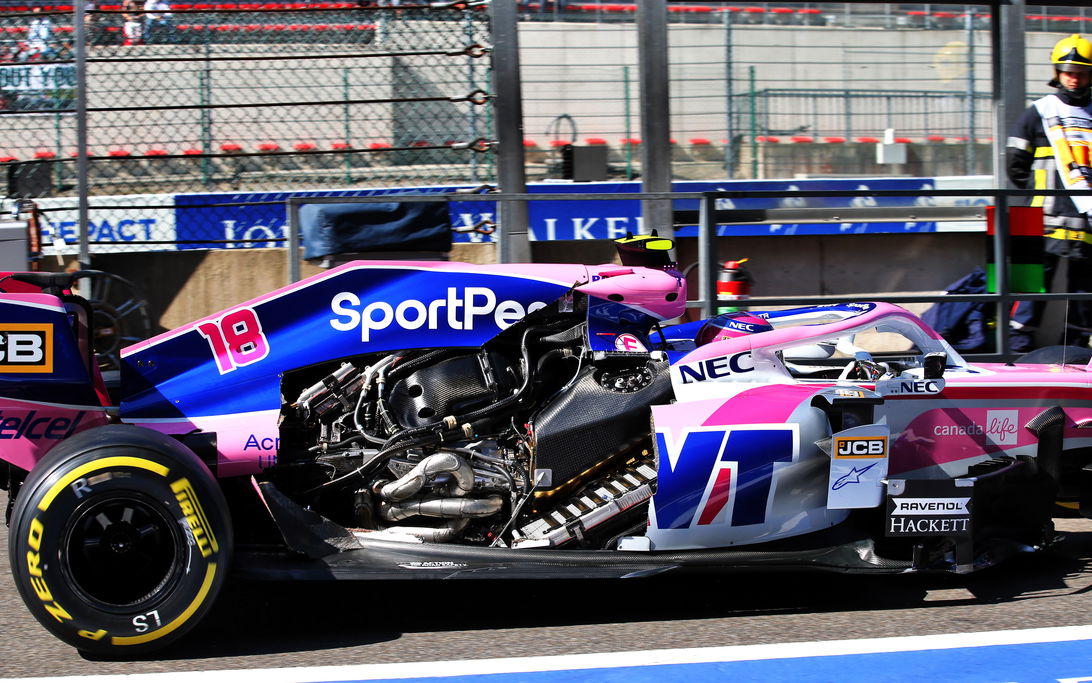
The engine of a Formula 1 car
The engine of a Formula 1 car is a powerful 1.6-litre V6 turbo engine with hybrid technology. This engine produces about 1,000 hp, which is roughly equivalent to the power of ten passenger cars. The engine is designed to run at a high speed, up to 15,000 rpm. This rpm makes for an impressive sound and tremendous acceleration. But how exactly is that power generated?
Turbo F1
The turbocharger is an important part of the engine and allows more air to enter the engine, resulting in better combustion and more power. The turbocharger uses the engine's exhaust gases to drive a compressor, which then compresses the air in the engine. This creates higher air pressure in the engine, allowing more fuel to be burned and producing more power. The turbocharger runs at high speed and can reach up to 125,000 rpm.
MGU-H - What is an MGU-H F1?
The MGU-H, or Motor Generator Unit - Heat, is a component of hybrid technology in the Formula 1 car engine. The MGU-H uses the energy from the engine's exhaust gases to generate electricity. This electricity is stored in the car's batteries and can then be used to power the MGU-K (Kinetic). The MGU-H is an important part of the engine because it ensures that less energy is lost in the exhaust gases, and this energy is converted into extra power.
MGU-K - What is an MGU-K F1?
The MGU-K (Motor Generator Unit - Kinetic) is another important part of the Formula 1 engine. This component converts kinetic energy (motion energy) into electricity, which is then stored in the battery. The MGU-K is used to increase the car's power output during acceleration and braking. During braking, the car's kinetic energy is converted into electricity and stored in the battery, which can later be used to provide additional power during acceleration. It is therefore vital that the driver uses the MGU-K efficiently to optimise the car's performance. The MGU-K in a Formula 1 car can produce a maximum of 120 kW, which is about 160 hp. To avoid an electric boost at the start, the use of the MGU-K is prohibited when the car travels less than 100 kilometres per hour. This motor-generator unit weighs no more than 7 kilograms and can make up to 50,000 revolutions per minute, with torque not exceeding 200 Nm. The MGU-H is 3 kilograms lighter and can even make up to 125,000 revolutions per minute.
ERS (Energy Recovery System)
The ERS takes energy from the heat of the exhaust and brakes and converts it into electrical power. This can be fed directly to the electric motors or stored in a battery for later use by the driver. The Motor Generator Unit - Kinetic [MGU-K] is an electric motor linked to the crankshaft of the engine. In regenerative mode, it acts as a generator that brakes the car, reducing the use of the brakes and generating electricity to charge the battery. In driving mode, the MGU-K acts as a motor that provides extra acceleration by using electricity to drive the wheels. The system has limited power per lap and is allowed to operate at full power for a maximum of 33 seconds. It can store up to twice the generated energy for later use. Teams can use this stored energy at strategic moments.
What is ERS F1?
The Motor Generator Unit - Heat [MGU-H] works in conjunction with the turbocharger and is more complex. The turbo uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine that pressurises the engine. As a generator, the MGU-H provides resistance to slow down the turbo's rotation and prevent overheating. The energy released during deceleration is converted into electricity and stored in the battery. The MGU-H is used as a motor to keep the turbocharger running when the throttle is not pressed, reducing turbo lag and making the release of power smoother than with a fuel engine. Importantly, the electricity generated by the MGU-H can be used to power the MGU-K, on top of the 33-second maximum power. This means that the more electricity teams can extract from the MGU-H, the longer they can use extra electrical power. The entire ERS system must weigh at least 150 kilograms, of which 20 to 25 kilograms are reserved for the storage part.
Fuel F1
The fuel used in Formula 1 is a very high-quality blend of petrol and ethanol, which meets strict FIA standards. The aim of this fuel is to create optimal combustion while minimising fuel consumption. Fuel consumption is limited by means of a fuel limit, which means that each car is only allowed to use a limited amount of fuel during a race. This creates additional challenges for drivers and teams during the race, as they have to make sure the engine uses the available fuel efficiently.
How many Power Units are Formula 1 teams allowed to use per season?
There used to be no restrictions on the use of engines, which cost teams a lot of money on special qualifying engines, for example. To reduce costs, there are now limits on the number of power units that can be used. Each driver may use no more than three internal combustion engines, three turbochargers, three MGU-Hs, three MGU-Ks, two storage batteries, two control electronics and eight exhaust systems per season.
Is the electric motor of a Formula 1 car dangerous?
A Formula 1 car's ERS system can deliver a dangerous shock of up to 1,000 volts. To reduce this risk, the high-voltage cables are coloured orange and equipped with a circuit breaker when disconnected. All components where high voltage is present are marked with warning signals and the ERS system can be switched off in various ways. At the top of the airbox are lights indicating the status of the ERS system. Green means it is safe and red means it is unsafe. Although incidents are thankfully rare, driver Daniel Ricciardo had to exit the car in 2019 without touching it because the red light came on and Renault concluded that the car was electrically unsafe.
New Formula 1 engines in 2026
In 2026, there will be new engine rules in Formula 1. Wondering what will be different? You can read all about it in this article.
Don't miss out on any of the Formula 1 action thanks to this handy 2026 F1 calendar that can be easily loaded into your smartphone or PC.
Download the calender